Collectively called immunoglobulinsabbreviated as Ig they are among the most abundant proteincomponents in the blood constituting about 20 of the total protein in plasma by weight. The researchers also looked for evidence that the B-cells had switched the types of antibody they produced.
Types Of Antibodies Mbl Life Science Japan
But only attaching to some of these sites will actually inactivate the virus.

. Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called B lymphocytes or B cells. First an animal like a mouse rabbit etc is immunized with a suitable antigen that corresponds to the desired monoclonal antibody we are interested in. For example different B cells in the body will produce multiple different antibodies that stick to different sites on the virus.
This is done by injecting antigens that are previously emulsified with some adjuvants like Freunds adjuvant. When an antigen is detected antibodies are produced to fight off infection. Antibodies are not found at a place as such but whenever our immune system encounters antigen or a pathogen B cells get activated immediately releasing antibodies into the bloodstream.
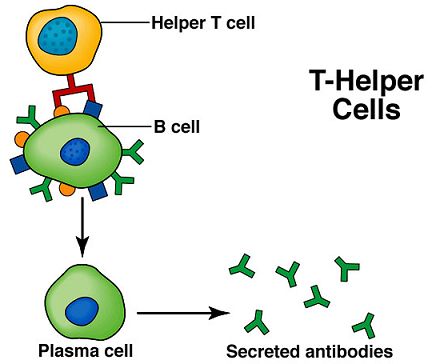
These cells trigger the B lymphocytes to produce antibodies. IgE binds to an allergen triggering a release of histamine which causes allergy symptoms. Each antibody binds with a different antigen A foreign substance that invades the body is called an antigen.
Synthesized exclusively by B cells antibodies are produced in billions of forms each with a different amino acidsequence and a different antigen-binding site. Each B cell lymphocyte produces one unique antibody against one unique epitope. Antibodies and their responding antigens fit together like a.
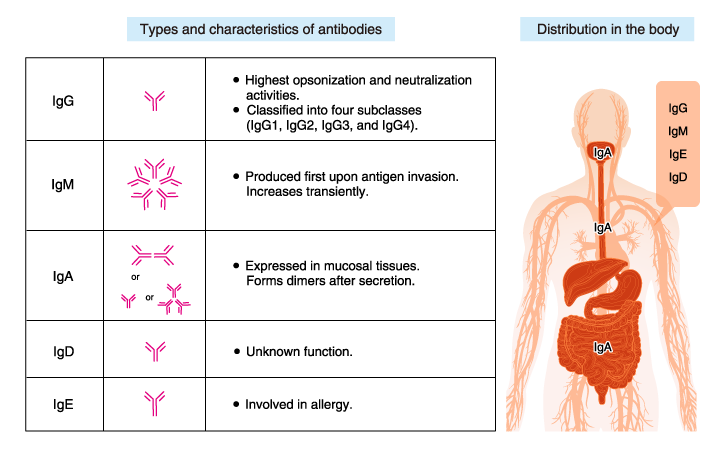
Once antibodies with sufficient specificity to the epitope can be encoded the B cell begins to release antibodies into the bloodstream. Antibodies can come in different varieties known as isotypes which refer to the genetic variations or differences in the constant regions of the heavy and light chains of the. 12 points It is estimated that humans can produce 1015 to 1018 different antibodies.
Primates including humans can produce 1 X 108 different IgG antibodies in blood serum to defend against the range of pathogens. When an antigen binds to the B-cell surface it stimulates the B cell to divide and mature into a group of identical cells called a clone. This switching process allows the immune system to customize its response to incoming threats.
Antibodies are made by B lymphocyces whice blood cells-which are readily available in human blood and which produce different types of antibodies. Each B-cell starts out as a single cell that makes a certain type of antibody Horns said. Pathogens can alter their surface antigens.
Describe four outcomes of an antigen-antibody reaction. This allows different daughter cells from the same activated B cell to produce antibodies of different isotypes or subtypes eg. However if the pathogen undergoes antigenic variation by the time the body mounts an immune response against a pathogen the pathogen has already altered its antigens and is unaffected by the.
It is able to take in extracellular antigens and present that antigen to T cells which may result in their activation Describe how a human can produce different antibodies. IgE also helps to fight parasitic infections. Describe how a human can produce different antibodies.
The development of clones of B and T cells against a specific antigen. Key Terms isotype. These immunoglobulins undergo mitosis resulting in cell division and continuously produce antibodies as a result of producing more cells.
A foreign substance that invades the body is called an antigen. When an antigen is detected several types of cells work together to recognize and respond to it. When an antigen is detected several types of cells work together to recognize and respond to it.
When an antigen is detected several types of cells work together to recognize and respond to it. Clonal deletion eliminates harmful B cells Describe how a human can produce different antibodies. It has been estimated that the human body can develop immune response against as many as 100 million or more different antigenic determinants which means that the body can produce as many different clones of B-lymphocytes each carrying a specific receptor.
In class we discuss mechanisms by which humans with only 22000 different protein-coding genes can produce that. By this mechanism alone a human can produce 287 different V L regions 200 κ and 116 λ and 8262 different V H regions. This method involves the following steps.
When it binds to a pathogen it prompts the. The receptors of B-cells are antibodies which bind to the antigenic determinants. A foreign substance that invades the body is called an antigen.
IgM is one of the first antibodies called in to fight infection. These cells trigger the B lymphocytes to produce antibodies. IgE is the antibody responsible for allergic reactions.
So for a vaccine to work it must produce this neutralizing antibody. With respect to antibody production and their ability to bind antigens describe how an. In people with autoimmune diseases IgG can trigger a symptom flare.
Once the B lymphocytes have produced antibodies these antibodies continue to exist in a persons body. Diagram an IgG antibody labeling the Fab Fc regions H chains L chains hinge region. The combinatorial diversification resulting from the assembly of different combinations of inherited V J and D gene segments just discussed is an important mechanism for diversifying the antigen-binding sites of antibodies.
These substances known as antigens can be present on bacteria toxins viruses tumor cells proteins or even normal cells. Indicate where antigen binding occurs and where binding to the FcεRI receptor occurs. Normally in the presence of antigens the body produces antibodies which can bind to the antigens and inactivate or destroy them.
The mature B cells called plasma cells secrete millions of antibodies into the bloodstream and lymphatic system. These cells trigger the B lymphocytes to produce antibodies. Each B lymphocyte makes only one type of antibody aimed at one antigen.
Antibodies and their responding antigens fit together like a key and a lock.

How Are Antibodies Produced Sino Biological

How Are Antibodies Produced Sino Biological
Immune System Antibody Tissue Rejection Biology Notes For Igcse 2014
0 Comments